How can generative AI be used in business? What new opportunities does the technology unlock, and what are its limitations? Like any emerging solution, generative AI raises questions and sometimes concerns because it introduces entirely new ways of working. The following examples around text generation illustrate this shift.
The Future of Banking: How Digital Transformation Enhances Customer Experience
See moreWhile many applications of generative AI are still to be developed, it can already be leveraged for concrete use cases that create real business value. In fact, automatic content creation tools have been around for several years. Generative AI has simply advanced these tools, making them more effective and more impactful.
Use case 1: the evolution of chatbots and voicebots in automated customer service contexts
Chatbots are a clear example of how generative AI is driving progress. Already part of our daily lives, conversational bots did not need generative AI to be effective in many use cases. Well-known examples include virtual assistants that guide customers on the web to the right product, page, information, or contact. What generative AI brings, however, is an additional layer of fluency and relevance in responses.
Until now, bot responses were fairly standardized, and interactions often ended up being handed over to a human agent. With training based on vast and diverse information sources, generative AI enables much more complex and capable models. These models offer a finer understanding of questions and, in turn, higher-quality responses. As a result, companies can significantly raise the standard of their chatbots and voicebots. The outcome is a better customer experience and higher satisfaction.
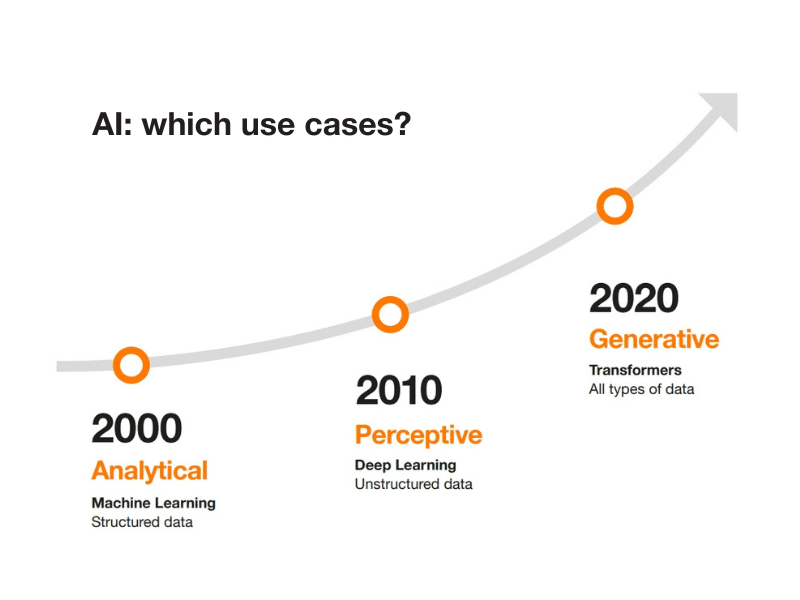
Use case 2: creating a help center or a knowledge base
Another application, closely related to chatbots, is the intranet, the specialized agent, or the search engine. These tools often rely on document or information indexing, with results that can vary in quality. Generative AI could transform this experience by turning all searches into natural language queries, making the process more user-friendly and consolidating information to provide more precise answers.
Take HR as a concrete example. By integrating all HR information into the intranet, employees could simply ask their questions and instantly receive either the right document or the requested information in a “natural” response, similar to what an HR colleague might provide. The same applies to specialized agents trained on a dedicated knowledge base. In the context of a scientific thesis, for instance, an integrated engine could use keywords to point directly to the relevant section or generate a concise summary of a topic or category.
Generative AI could therefore make search engines behave more like Google: instead of typing keywords and browsing through several pages of results, it could synthesize the most relevant pages and deliver an easy-to-read summary. This represents a genuine use case for an enhanced search engine, supported by an agent with access to extensive knowledge bases. We deliberately avoid speaking of “optimal search,” however, because the information used may contain errors. Natural language tends to create the illusion of truth, yet in AI, absolute truth does not exist.
Use case 3: automatic code generation
While business use cases are numerous, generative AI also provides strong support for developers by automating code generation, saving them considerable time. The principle is straightforward: describe a problem in natural language, and the tool can generate several hundred lines of high-quality code.
Unlike traditional code generation, generative AI introduces a truly interactive dimension combined with unmatched speed. While many tools on the web can already handle such tasks, the major difference lies in how generative AI turns “something close to what I’m looking for” into “exactly what I need.”
Cas d’usage n°4 : la génération de données
Generative AI can be applied to a wide range of business use cases. However, it is important to understand that its performance comes from the “extraordinary” volume of data used to train it. Chatbots, for example, need access to information to provide accurate and relevant responses. Data is therefore the sine qua non condition for developing generative AI use cases in the enterprise. Without data, there is no data project and, ultimately, no AI.
That said, without going to the extreme case of having no data at all, companies often have at least some datasets available, whether small or large. Generative AI can not only learn from these datasets but also create additional synthetic data. The idea is to enrich and diversify the dataset from a sample, which helps improve machine learning models. As a result, it becomes possible to build models with minimal configuration.
For instance, when developing software, it is standard practice to use test data before going live. Generative AI can generate these test datasets, making the development process faster and more efficient.
Use case 5: creating creative content
Another strong use case for generative AI lies in its creative capabilities. While most use cases focus on text-based AI designed to inform, generative AI is equally capable of producing creative outputs. Marketing and communication are particularly well suited, for example through the generation of images to illustrate articles. In this context, generative AI becomes an additional visual resource, meeting needs for speed and scale. Some projects involve urgent demands, and marketing teams could simply ask their content generation solution to create a visual, which they could refine afterwards if needed, saving valuable time. Tools such as DALL-E (also from OpenAI) or Midjourney already allow images to be generated directly from text descriptions.
In a completely different domain, generative AI enables a new level of human behavior simulation. Similar to what is seen in video games, professional use cases can emerge in training or in remotely operating certain industrial activities. Imagine, for instance, a virtual or augmented reality headset capable of reproducing precise human gestures in different scenarios.
These tools are still new, and many generative AI use cases are still emerging. As a result, there is little historical data on actual outcomes. This lack of feedback leads many companies to remain hesitant about venturing into content generation. How far can it go? What limitations will arise around information production? Another key issue is that these powerful technologies are deeply rooted in the cloud, raising questions about data ingestion and confidentiality.
In any case, we are witnessing continuous evolution—not linear progression—since AI is already reshaping the way we work. In some situations, generative AI will bring incremental improvements. In others, it will enable entirely new use cases or unlock higher levels of performance. This is where data and AI experts like Orange Business have a key role to play in raising awareness and guiding organizations. Achieving the same quality of responses as public tools such as ChatGPT requires not just large amounts of data, but data of high quality as well.













Comments (0)
Your email address is only used by Business & Decision, the controller, to process your request and to send any Business & Decision communication related to your request only. Learn more about managing your data and your rights.